C vs Embedded C
Introduction
C is one of the most widely used programming languages, known for its efficiency, portability, and power. However, when it comes to embedded systems, a variation of C known as Embedded C is often used. While both share fundamental similarities, there are distinct differences in their purpose, application, and execution. In this blog, we will delve deep into C vs Embedded C, highlighting their differences, similarities, and use cases.
What is C?
C is a high-level, general-purpose programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie in the early 1970s. It provides low-level access to memory and supports structured programming, making it a preferred choice for system-level programming, application development, and operating systems.
Features of C:
- Simple and structured language
- Portability across different platforms
- Supports functions, arrays, pointers, and structures
- Provides direct access to hardware through pointers
- Efficient use of memory and CPU
C is commonly used in application software, operating system development (e.g., Linux), game development, and desktop applications.
What is Embedded C?
Embedded C is an extension of the C programming language specifically designed for programming embedded systems. It includes additional libraries and features to interact with hardware components like microcontrollers, sensors, and memory devices.
Features of Embedded C:
- Similar syntax and structure to standard C
- Includes hardware-specific libraries
- Direct access to microcontroller registers and memory
- Uses real-time constraints and event-driven programming
- Optimized for low power consumption and efficiency
Embedded C is widely used in firmware development, automotive systems, medical devices, industrial automation, and IoT applications.
Key Differences Between C and Embedded C
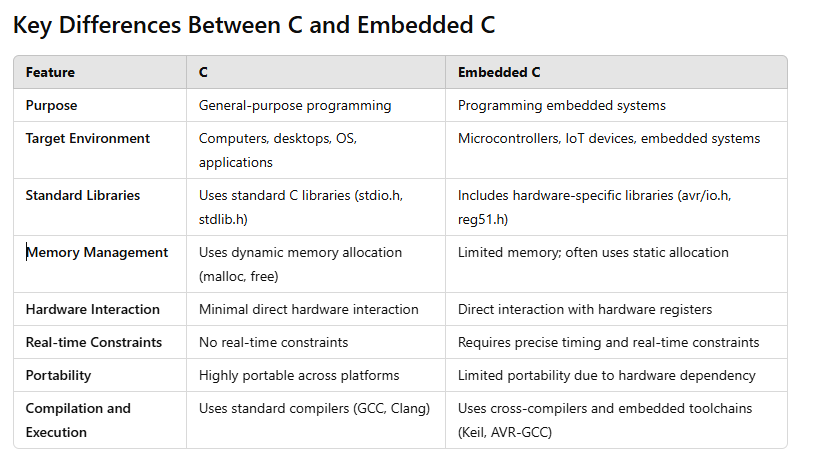
Similarities Between C and Embedded C
Despite their differences, C and Embedded C share many similarities:
- Syntax and Structure: Both languages follow the same syntax, including loops, conditional statements, and functions.
- Data Types: Common data types such as
int,char,float, anddoubleare used in both. - Operators: Both use arithmetic, logical, and bitwise operators.
- Control Statements: If-else, loops (for, while), and switch-case structures are common.
- Functions and Modular Programming: Code reusability and modularity principles are maintained in both.
Example Codes
C Program Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
return 0;
}Embedded C Program Example (Blinking LED on a Microcontroller):
#include <reg51.h>
sbit LED = P1^0; // Define LED at Port 1, Pin 0
void delay() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 30000; i++);
}
void main() {
while (1) {
LED = 1; // Turn ON LED
delay(); // Wait
LED = 0; // Turn OFF LED
delay(); // Wait
}
}When to Use C vs Embedded C?
- Use C when:
- Developing operating systems, compilers, or application software.
- Portability is required across multiple platforms.
- Memory and hardware control are not strict constraints.
- Use Embedded C when:
- Programming microcontrollers, IoT devices, and real-time applications.
- Direct interaction with hardware is necessary.
- Real-time performance and low power consumption are critical.
Conclusion
Both C and Embedded C play crucial roles in software and hardware development. While C is a general-purpose programming language suited for applications and operating systems, Embedded C is optimized for programming microcontrollers and embedded systems with real-time constraints. Understanding their differences helps developers choose the right language for their specific projects. Whether you are designing a software application or working on an embedded device, mastering both C and Embedded C will be an invaluable skill in the tech industry.
Read my other blogs:
C Program to find Given Number is Prime or not.
Write a program to find Factorial Numbers of a given numbers.
Embedded C language Interview Questions.
Automotive Interview Questions
Understanding AUTOSAR Architecture: A Guide to Automotive Software Integration
Big Endian and Little Endian in Memory
Zero to Hero in C language Playlist
Embedded C Interview Questions
Subscribe my channel on Youtube: Yogin Savani
